Medical tubing is an essential component of many medical devices, including catheters, IV sets, and blood transfusion sets. Medical tubing is typically made from a variety of materials, including silicone, PVC, and polyurethane, and can be produced in a range of sizes and configurations to meet specific medical needs. The process of producing medical tubing typically involves extrusion, cutting, and assembly, as well as various quality control measures.
Extrusion is the process of melting the raw material and then forcing it through a die to create a tube of the desired size and shape. The first step in the extrusion process is to prepare the raw material by mixing it with any necessary additives, such as stabilizers or colorants. The material is then fed into an extruder, which heats the material to a specific temperature and applies pressure to force the molten material through a die. The die determines the size and shape of the tube and may include features such as ridges or flanges for connecting to other components.
After the tube is extruded, it is typically cooled and then cut to the desired length. Cutting can be done using a variety of methods, including guillotine cutting, rotary cutting, and laser cutting. Guillotine cutting involves cutting the tube with a sharp blade, while rotary cutting uses a rotating blade to cut the tube. Laser cutting uses a focused beam of light to cut the tube and is typically used for more precise cuts.
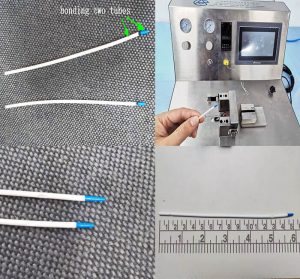
After the tube is cut to the desired length, it may be assembled with other components to create a finished medical device. Assembly can involve a variety of techniques, including welding, bonding, or crimping. For example, in the case of an IV set, the tubing may be attached to a needle, a drip chamber, and a bag of saline solution using welding or bonding techniques.
Quality control is an essential part of the medical tubing production process. Quality control measures may include visual inspection, testing for leaks, and checking the dimensional accuracy of the tubing. Visual inspection involves examining the tubing for defects such as air bubbles, foreign particles, or discoloration. Testing for leaks involves pressurizing the tubing and checking for any signs of leakage. Checking the dimensional accuracy of the tubing involves measuring the diameter, thickness, and length of the tubing to ensure it meets the required specifications.
There are several factors to consider when selecting the appropriate process for producing medical tubing, including the material being used, the desired size and shape of the tubing, and the required production volume. Different materials may require different extrusion temperatures and pressures, and may have different tolerances for cutting and assembly. Additionally, the desired size and shape of the tubing will affect the choice of extrusion die, and the required production volume will influence the choice of cutting and assembly methods.
In addition to the basic processes described above, there are several advanced techniques that can be used to produce high-quality medical tubing. For example, coextrusion involves extruding multiple layers of different materials simultaneously to create tubing with specific properties, such as resistance to kinking or puncture. Similarly, crosslinking can be used to improve the strength and durability of medical tubing by increasing the molecular bonds between polymer chains.
In conclusion, the process of producing medical tubing is a complex and important part of the medical device manufacturing industry. The process typically involves extrusion, cutting, and assembly, as well as various quality control measures. There are several factors to consider when selecting the appropriate process for producing medical tubing, including the material being used, the desired size and shape of the tubing, and the required production volume. Additionally, there are several advanced techniques that can be used to produce high-quality medical tubing, such as coextrusion and crosslinking. Overall, the production of medical tubing requires careful attention to detail and a commitment to producing